Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Brca1 Screening Guidelines
Swiss guidelines for genetic counseling and testing for breast and ovarian cancer predis-position The present paper summarises the Swiss guidelines for genetic counseling and ultimately testing individu-als with an increased probability for carrying muta-tions in high-risk breastovarian cancer predisposition genes particularly BRCA1BRCA2. Individuals at 10 risk of carrying a mutation are eligible for NHS testing as outlined in NICE.
 Brca Mutation Carriers Breast And Ovarian Cancer Screening Guidelines And Imaging Considerations Radiology
Brca Mutation Carriers Breast And Ovarian Cancer Screening Guidelines And Imaging Considerations Radiology
Based on NCCN Guidelines and UCSF Center for BRCA Research Steering Committee Updated March 2018 BRCA1 Mutation Positive Guidelines Breast Cancer Education Breast self-awareness beginning at age 18 Seek medical evaluation for changes in the breast The majority of breast cancers in women with a BRCA1 mutation are triple-negative.

Brca1 screening guidelines. Pathogenic mutations of the BRCA12 genes are associated with a high risk of breast ovarian fallopian tube and peritoneal cancer in women male breast cancer and to a lesser degree pancreatic and aggressive early-onset prostate cancer. Two major changes from previous USPSTF recommendations address the inclusion of two additional patient groups. If you have any questions or comments please email.
Have a known BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation based on having had genetic testing Have a first-degree relative parent brother sister or child with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation and have not had genetic testing themselves Had radiation therapy to the chest when they were between the ages of 10 and 30 years. A known BRCA1 BRCA2 or other inherited mutation in your family Genetic testing for hereditary breast and ovarian cancer looks for mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. ACOG Guidelines for Managing Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations.
There are also specific guidelines focusing on breastovarian hereditary cancer syndromes including cancer prevention and screening among individuals known to harbour a pathogenic BRCA12 mutation. Frequently asked questions. Aged 2029 years with a known BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation.
Although there are no NCCN guidelines for colorectal cancer screening of BRCA mutation carriers women younger than 50 years with BRCA1 mutations should consider undergoing colonoscopy every 35 years beginning at age 40 years 4492. Individual with any of the following. BRCA Screening Can Save Lives The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are tumor suppressor genes.
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network NCCN guidelines recommend that men with harmful germline variants in BRCA1 or BRCA2 consider having a discussion with their doctor about prostate-specific antigen PSA testing for prostate cancer screening starting at age 40. Approximately 10 percent of ovarian cancer cases and 3 to 5 percent of breast cancer cases. BRCA testing is only recommended for people with a high risk of having BRCA mutations.
If there is a low chance of finding a BRCA mutation your ob-gyn or other health care professional may not recommend genetic testing. Who is eligible for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation termed BRCA testing. BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation testing guidelines.
Aged 5069 years with a known BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation unless mammography has shown a dense breast pattern. Aged 5069 years who have not had genetic testing but have a greater than 30 probability of being a BRCA or a TP53 carrier unless mammography has shown a dense breast pattern. Establish clinical guidelines on BRCA testing to 1 identify individuals who may benefit from risk-reducing strategies 2 update recommendations of testing for theragnostic purposes with PARPi agents in BRCA-related cancer 3 provide recommendations for testing for personalised management of early and metastatic breast cancer and 4 define the place and role of a tumour testing.
Based on this evidence women with BRCA1 mutations should be counseled about their increased risk for early-onset colorectal cancer and offered colonoscopy at 3- to 5-year intervals between the ages of 40 and 50 years and should follow population guidelines thereafter. Your doctor might suggest testing using a multigene panel which looks for mutations in several genes at the same time including BRCA1 and BRCA2. 1 women with previous breast cancer or ovarian cancer who are considered cancer-free.
Living affectedindividual proband with breast or ovarian cancer where the individual - family history meets one of the criteria. The initial screening for hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome. Risk Assessment and Counseling.
It is important to remember that most cases of breast and ovarian cancer are not caused by gene mutations. Criteria for BRCA1 and BRCA2 testing. The ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines CPG are intended to provide the user with a set of recommendations for the best standards of cancer care based on the findings of evidence-based.
USPSTF released updated guidelines 2019 to help primary care professionals identify women who would benefit from further genetic counseling and testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2.
 New Algorithm For Brca1 2 Testing Download Scientific Diagram
New Algorithm For Brca1 2 Testing Download Scientific Diagram
 Specificity Of Criteria For Brca1 2 Testing Download Table
Specificity Of Criteria For Brca1 2 Testing Download Table
Breast Cancer Overview Risk Factors Screening Genetic Testing And Prevention
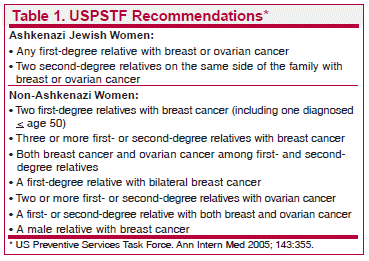 Brca Screening The Medical Letter Inc
Brca Screening The Medical Letter Inc
 Expert Recommendations For Screening Brca Mutation Carriers For Breast Download Table
Expert Recommendations For Screening Brca Mutation Carriers For Breast Download Table
 Brca Genetic Mutations Brcaness
Brca Genetic Mutations Brcaness
Https Canpweb Org Canp Assets File 2017 20conference Presentations Hereditary 20cancer 20 20chaudhary Pdf
 Recommendations For The Implementation Of Brca Testing In Ovarian Cancer Patients And Their Relatives Sciencedirect
Recommendations For The Implementation Of Brca Testing In Ovarian Cancer Patients And Their Relatives Sciencedirect
 Screening Recommendations Condensed Download Table
Screening Recommendations Condensed Download Table
 Swedish Breast Cancer Group Brca 1 And Brca 2 Screening Criteria Download Scientific Diagram
Swedish Breast Cancer Group Brca 1 And Brca 2 Screening Criteria Download Scientific Diagram
 Brca Associated Cancers Role Of Imaging In Screening Diagnosis And Management Radiographics
Brca Associated Cancers Role Of Imaging In Screening Diagnosis And Management Radiographics
 A Systematic Review Of International Guidelines And Recommendations Fo Cmar
A Systematic Review Of International Guidelines And Recommendations Fo Cmar
 Pdf Screening Brca1 And Brca2 Mutation Carriers For Breast Cancer
Pdf Screening Brca1 And Brca2 Mutation Carriers For Breast Cancer
 Brca Mutation Carriers Breast And Ovarian Cancer Screening Guidelines And Imaging Considerations Radiology
Brca Mutation Carriers Breast And Ovarian Cancer Screening Guidelines And Imaging Considerations Radiology
Comments
Post a Comment