Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Whole Exome Sequencing Vs Whole Genome Sequencing
However one of the practical concerns is the potential false negatives due to incomplete breadth and depth of coverage for several exons in clinically implicated genes. Research vs clinical applications.
Get a clear comparison of the applications of whole-genome sequencing.
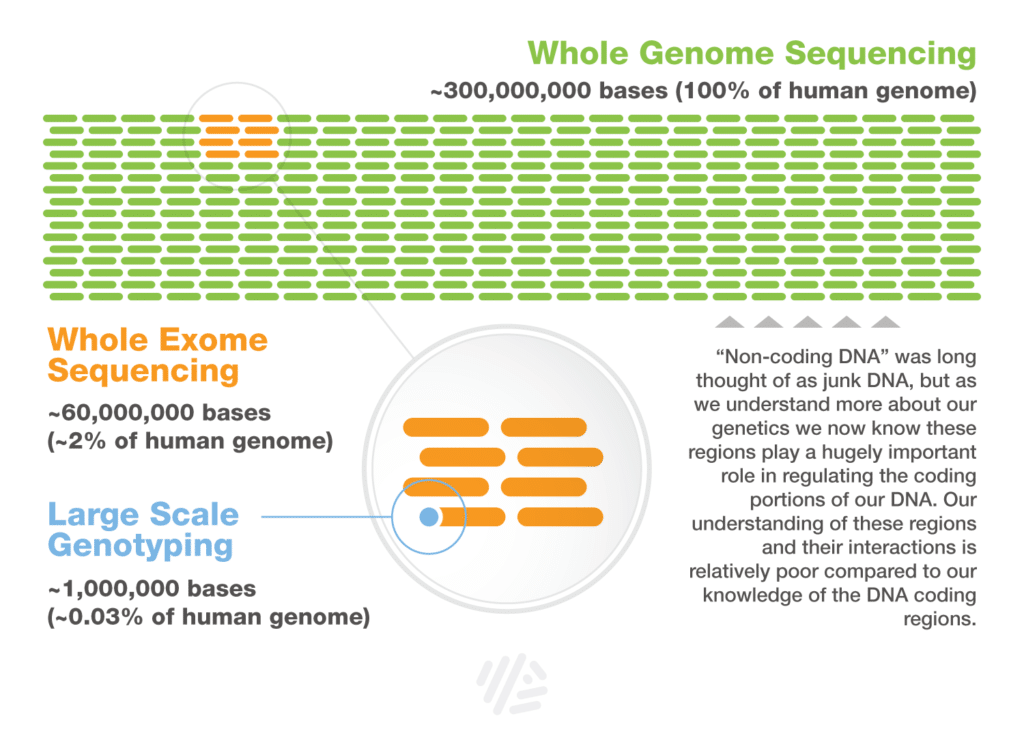
Whole exome sequencing vs whole genome sequencing. Together all the exons in a genome are known as the exome and the method of sequencing them is known as whole exome sequencing. The widespread availability of NGS technologiesincluding whole genome sequencing WGS and whole exome sequencing WEShas not only led to its applications in cancer research but also for use in the clinical setting 34. Exomes are the part of the genome formed by exons or coding regions which when transcribed and translated become expressed into proteins.
Because most known mutations that cause disease occur in exons whole exome sequencing is thought to be an efficient. We analyzed concordance between ctDNA and whole-exome sequencingwhole-genome sequencing WESWGS of tumor samples from patients with breast n 12 gastrointestinal n 20 lung n 19 and other tumor types n 13. Whole-genome sequencing is somewhat contrived.
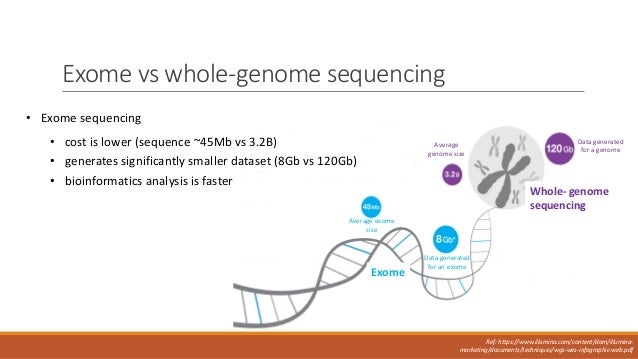
Exome sequencing is a powerful tool for characterizing DNA sequences surrounding target regions at a much lower cost compared to the whole-genome sequencing technique 9. Physicians and drug companies are more interested in yesno answers which is why genomic panels comprised of anywhere from a dozen to several hundred genes are where the future of medical sequencing lies. In some cases researchers have analyzed exome sequencing data from only one patient 45 whereas most studies have used exome sequencing data from several members of an afflicted family 6-8.
While whole genome sequencing approaches can capture all possible mutations whole exome or targeted gene panel sequencing are cost-effective approaches for capturing phenotype altering mutations. Coverage uniformity with WGS is superior to WES. While whole genome sequencing WGS provides complete sequencing of a genome data analysis constraints and the high cost of WGS have led to the development of more cost-effective whole exome sequencing solutions.
The human exome represents less than 2 of the genome but contains about 85 of known disease-related variants making this method a cost-effective alternative to whole-genome sequencing. Sequencing is a technique that determines the precise order of the nucleotides in a particular DNA. Correlation in the driver hotspot and actionable alterations was studied.
Whole exome sequencing is a commonly used next-generation sequencing NGS procedure which involves the sequencing of protein-coding regions of the genome. On the other hand Whole Genome Sequencing reveals the full 100 of your DNA that includes all 3 billion base pairs only 40 million base pairs are. WGS has more reliable sequence coverage.
Since whole exome sequencing decodes only 1 of the genome it fails to analyze the other 99 including structural and non-coding regions. Circulating tumor DNA ctDNA is believed to overcome these limitations. One frequent question we hear on Genohub is should I make a custom panel for this gene set or not bother and do whole exome sequencing.
Exome sequencing is widely used for the. Interested in the role that whole-genome sequencing plays across the research space and curious as to how the technology translates into clinical practices. In some cases a targeted gene panel testing may be a dependable option to ascertain true negatives for genomic variants in known.
Exome sequencing is a targeted sequencing approach that interrogates only the disease-causing exonic regions of the genome. Cancer research PCR and sequencing Whole-genome studies. Differences in the hybridization efficiency of WES capture probes can result in regions of the genome with little or no coverage.
Exomes compose only about 2 of the whole genome. Whole-exome sequencing WES is gradually being optimized to identify mutations in increasing proportions of the protein-coding exome but whole-genome sequencing WGS is becoming an attractive alternative. WGS is currently more expensive than WES but its cost should decrease more rapidly than that of WES.
Whole Genome Sequencing WGS and Whole Exome Sequencing WES are increasingly clinically avalai bel due to significant advances in DNA sequencing technology over. The key difference between whole genome sequencing and exome sequencing is that the whole genome sequencing sequences the entire genome of an organism while the exome sequencing sequences only the exome or the protein-coding genes of an organism. The most important difference between whole exome and whole genome sequencing is the amount of DNA sequenced.
Three cases in which more-in-depth genomic. This method allows variations in the protein-coding region of any gene to be identified rather than in only a select few genes. WES omits regulatory regions such as promoters and enhancers.
The exome may be small compared with the whole genome but it is still quite large. Whole exome sequencing WES is widely adopted in clinical and research settings. The notion of exome vs.
Use of NGS has accelerated the discovery of somatic mutations 5 and germline mutations in Mendelian diseases 6.
 Cost Comparison Of Target Sequencing Panel Einstein V1 Versus Whole Download Table
Cost Comparison Of Target Sequencing Panel Einstein V1 Versus Whole Download Table
 Impact Of Next Generation Whole Exome Sequencing In Molecular Diagnostics Sciencedirect
Impact Of Next Generation Whole Exome Sequencing In Molecular Diagnostics Sciencedirect
 Table 1 From Whole Genome And Whole Exome Sequencing In Neurological Diseases Semantic Scholar
Table 1 From Whole Genome And Whole Exome Sequencing In Neurological Diseases Semantic Scholar
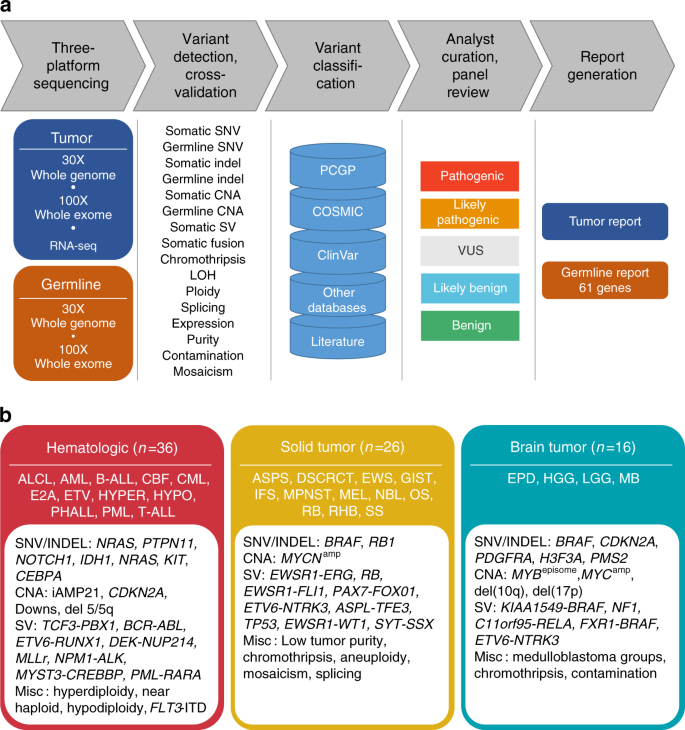 Clinical Cancer Genomic Profiling By Three Platform Sequencing Of Whole Genome Whole Exome And Transcriptome Nature Communications
Clinical Cancer Genomic Profiling By Three Platform Sequencing Of Whole Genome Whole Exome And Transcriptome Nature Communications
 Hanna Rennert Validation And Implementation Of Whole Exome Sequencing Youtube
Hanna Rennert Validation And Implementation Of Whole Exome Sequencing Youtube
 Verschil Tussen Whole Genome Sequencing En Exome Sequencing Moleculaire Biologie Het Verschil Tussen Vergelijkbare Objecten En Termen
Verschil Tussen Whole Genome Sequencing En Exome Sequencing Moleculaire Biologie Het Verschil Tussen Vergelijkbare Objecten En Termen
 Illustration Of The Whole Genome Whole Exome And Targeted Gene S Download Scientific Diagram
Illustration Of The Whole Genome Whole Exome And Targeted Gene S Download Scientific Diagram
 Comparison Of Targeted Panels Whole Exome Sequencing Wes And Download Table
Comparison Of Targeted Panels Whole Exome Sequencing Wes And Download Table
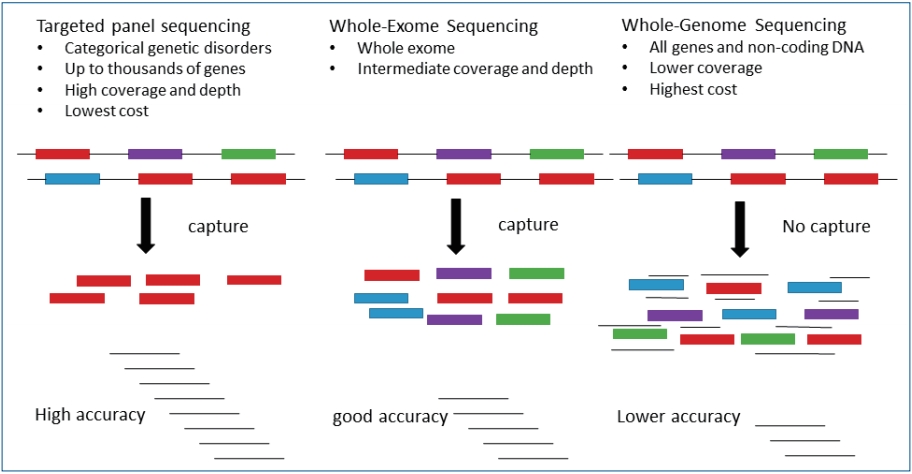 Genetic Tests By Next Generation Sequencing In Children With Developmental Delay And Or Intellectual Disability
Genetic Tests By Next Generation Sequencing In Children With Developmental Delay And Or Intellectual Disability
 Figure 3 From Human Genome Sequencing In Health And Disease Semantic Scholar
Figure 3 From Human Genome Sequencing In Health And Disease Semantic Scholar
 Whole Genome And Exome Sequencing My46
Whole Genome And Exome Sequencing My46
 What Is The Best Dna Test For Consumers Gene Food
What Is The Best Dna Test For Consumers Gene Food

Comments
Post a Comment