Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Clinical Whole Genome Sequencing
Cancer research PCR and sequencing Whole-genome studies. Genome-wide CNV analysis 50 kb was performed on a multicenter group of 570 patients using a low-coverage whole-genome sequencing pipeline.
 Study Overview Discovery Phase Whole Genome Sequencing Wgs Followed Download Scientific Diagram
Study Overview Discovery Phase Whole Genome Sequencing Wgs Followed Download Scientific Diagram
In situations involving nosocomial infection not only must confirmed positive cases be isolated but thorough intrahospital contact tracing must be performed to identify healthcare workers and.
Clinical whole genome sequencing. Whole-genome sequencing WGS is poised to exert a profound influence on clinical care by ushering. TruGenome undiagnosed disease cWGS test. Whole exome sequencing WES is widely adopted in clinical and research settings.
Given current resource and infrastructure limitations. The TruGenome Undiagnosed Disease test is designed to detect and report on. Clinical whole-genome sequencing offers a potential avenue for the identification of private genomic variation that may confer sensitivity to targeted agents and offer patients new options for targeted therapies.
Clinical utility of genomic sequencing. Whole exome sequencing WES is a method of analyzing the protein coding regions also called the exome which comprise 1-2 of the entire genome. With the advent of next-generation sequencing NGS technologies whole exome sequencing WES is widely used as a cost-effective and accurate method of genetic testing.
Whole genome sequencing WGS has had widespread use in the management of microbial outbreaks in a public health setting. This model although beneficial has multiple shortcomings especially for localised infection control. Research vs clinical applications.
In some cases a targeted gene panel testing may be a dependable option to ascertain true negatives for genomic. 3839 Whole-genome sequencing is expected to provide superior coverage of certain genomic regions including intronic and other noncoding regions associated with inherited disease noncoding. With the ability to.
We aimed to determine whether next-generation sequencing NGS technology could be an alternative method for CNV detection in routine clinical application. Variants of interest were. Clinical whole-genome sequencing WGS can detect a broad range of pathogenic allele types and is emerging as an effective first-tier test for cases in which physicians are faced with a high degree of diagnostic uncertainty 5.
However one of the practical concerns is the potential false negatives due to incomplete breadth and depth of coverage for several exons in clinically implicated genes. Whole-exome sequencing and analysis protocols developed by the Human Genome Sequencing Center at the Baylor College of Medicine were adapted for the clinical test of whole-exome sequencing. Quality control and identification of mutations variant calling of WGS within the cancer arm of 100000 Genomes is enabled through a standardised bioinformatics pipeline 5 8 9.
By comparison with testing for single nucleotide polymorphisms whole-genome sequencing. Clinical Whole Exome Sequencing CLIACAPISO17025 Genetic testing known as DNA testing allows geneticists to determine bloodlines and diagnose genetic diseases. Current models encompass sending isolates to a central laboratory for WGS who then produce a report for various levels of government.
Compared with present clinical genetic testing whole-genome sequencing greatly expands the breadth of testing from genes associated with a particular disease to the whole genome and potentially all the information that the genome contains about diseases or traits. Whole-exome sequencing has been the primary sequencing modality in clinical genetics and in surveys of reportable genetic findings in unselected participants. Clinical whole genome sequencing tests were philanthropically provided through Illuminas.
Methods Patient selection information. These samples were referred for chromosomal analysis. Whole-genome sequencing WGS is positioned to become one of the most robust strategies for achieving timely.
Interested in the role that whole-genome sequencing plays across the research space and curious as to how the technology translates into clinical practices. In the case of whole genome sequencing bioinformatic algorithms are required to create reports that contain the relevant clinically actionable information. Whole genome sequencing WGS using fresh frozen tissue and matched blood samples from cancer patients is becoming in reach as the most complete genet.
Genomics and whole genome sequencing WGS have the capacity to greatly enhance knowledge and understanding of infectious diseases and clinical microbiology. A measurement toolkit Abstract. Get a clear comparison of the applications of whole-genome sequencing.
For infection control within hospitals whole genome viral sequencing can help to determine whether newly diagnosed patients have nosocomial or community-acquired infections. The growth and availability of bench-top WGS analysers has facilitated the feasibility of genomics in clinical and public health microbiology. The Illumina Clinical Services Laboratory was the first clinical lab to generate a personal whole-genome sequence and remains a leading service provider today.
Clinical Genome Sequencing Services In 2009 we established a CLIA-certified CAP-accredited laboratory to offer clinical whole-genome sequencing services.
 Whole Genome Sequencing The New Standard Of Care Science
Whole Genome Sequencing The New Standard Of Care Science
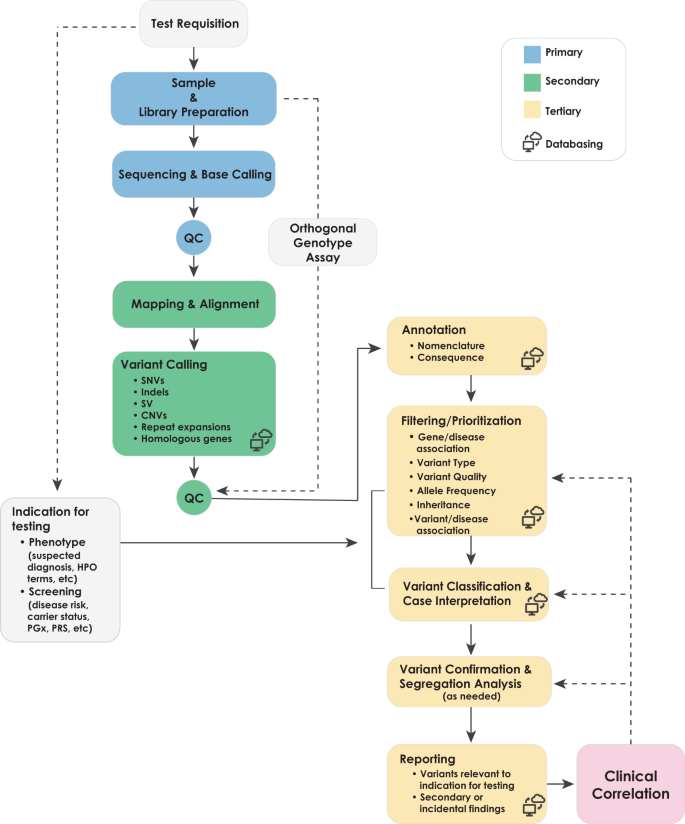 Best Practices For The Analytical Validation Of Clinical Whole Genome Sequencing Intended For The Diagnosis Of Germline Disease Npj Genomic Medicine
Best Practices For The Analytical Validation Of Clinical Whole Genome Sequencing Intended For The Diagnosis Of Germline Disease Npj Genomic Medicine
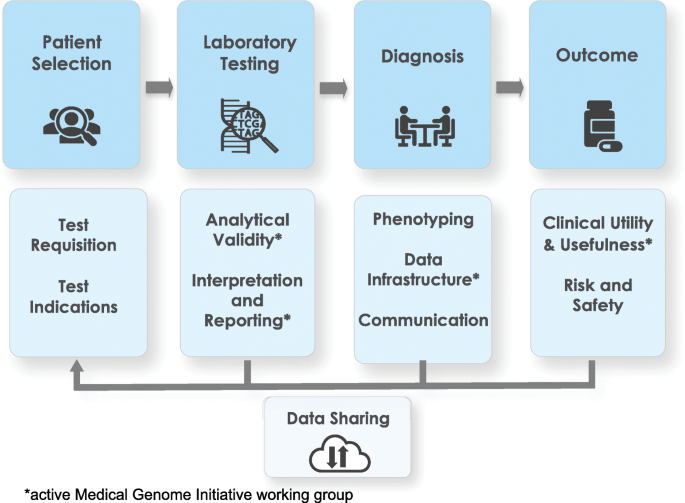 The Medical Genome Initiative Moving Whole Genome Sequencing For Rare Disease Diagnosis To The Clinic Genome Medicine Full Text
The Medical Genome Initiative Moving Whole Genome Sequencing For Rare Disease Diagnosis To The Clinic Genome Medicine Full Text
 Whole Genome Sequencing For Identification Of Mendelian Disorders In Critically Ill Infants A Retrospective Analysis Of Diagnostic And Clinical Findings The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
Whole Genome Sequencing For Identification Of Mendelian Disorders In Critically Ill Infants A Retrospective Analysis Of Diagnostic And Clinical Findings The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
 New Clinical Whole Genome Sequencing Service Nata Accredited Vcgs
New Clinical Whole Genome Sequencing Service Nata Accredited Vcgs
 Whole Genome Sequencing Is Feasible In Clinical Practice
Whole Genome Sequencing Is Feasible In Clinical Practice
Evidence Based Design And Evaluation Of A Whole Genome Sequencing Clinical Report For The Reference Microbiology Laboratory
 Clinical Whole Exome Sequencing Service Novogene
Clinical Whole Exome Sequencing Service Novogene
 Clinical Validation Of Whole Genome Sequencing For Cancer Diagnostics The Journal Of Molecular Diagnostics
Clinical Validation Of Whole Genome Sequencing For Cancer Diagnostics The Journal Of Molecular Diagnostics

 Study Cohort Overview Whole Genome Sequencing Top And Capture Download Scientific Diagram
Study Cohort Overview Whole Genome Sequencing Top And Capture Download Scientific Diagram
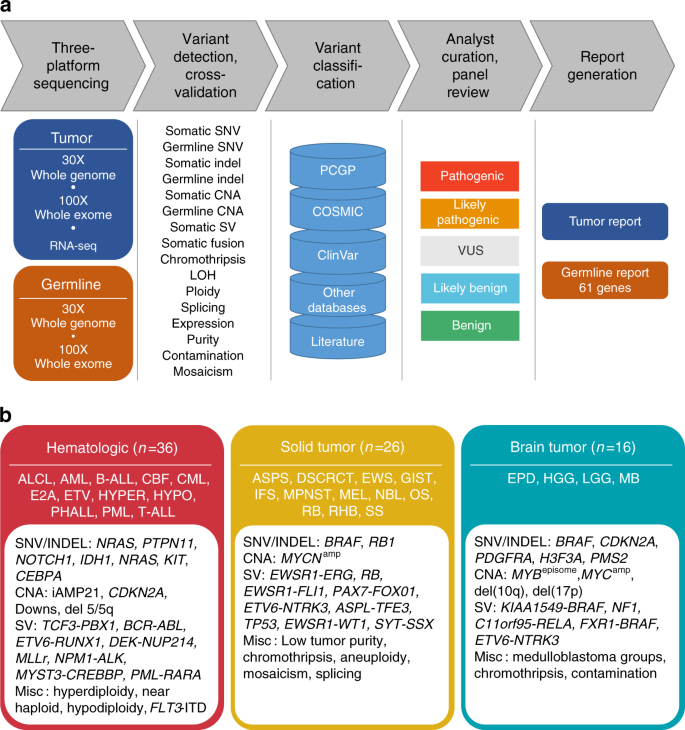
 Clinical Cancer Genomic Profiling By Three Platform Sequencing Of Whole Genome Whole Exome And Transcriptome Nature Communications
Clinical Cancer Genomic Profiling By Three Platform Sequencing Of Whole Genome Whole Exome And Transcriptome Nature Communications
 Clinical Whole Genome Sequencing As A First Tier Test At A Resource Limited Dysmorphology Clinic In Mexico Npj Genomic Medicine X Mol
Clinical Whole Genome Sequencing As A First Tier Test At A Resource Limited Dysmorphology Clinic In Mexico Npj Genomic Medicine X Mol
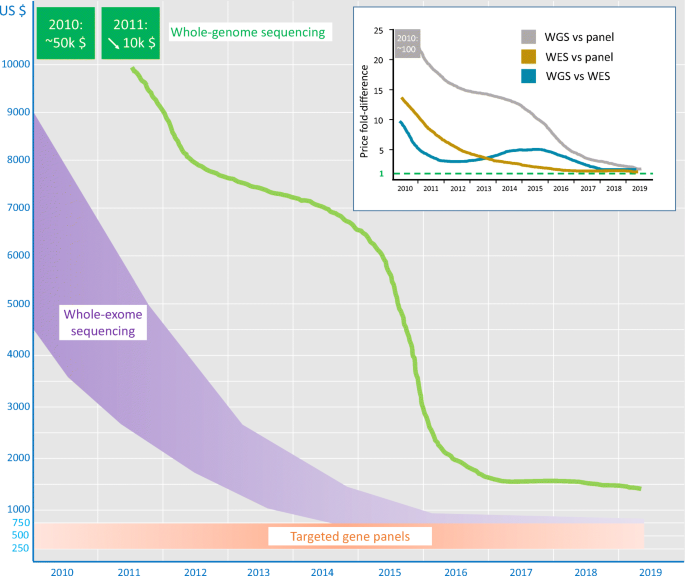 Advantages And Perils Of Clinical Whole Exome And Whole Genome Sequencing In Cardiomyopathy Springerlink
Advantages And Perils Of Clinical Whole Exome And Whole Genome Sequencing In Cardiomyopathy Springerlink
Comments
Post a Comment